Emedgene
Streamlined
Enable greater efficiency from your tertiary analysis workflows with explainable AI (XAI) and automation supporting genomes, exomes, virtual panels, and targeted panels.
Integrated
Unify your laboratory and NGS instrumentation with your IT systems to simplify and secure your complete workflow.
Powered for growth
Confidently keep pace with evolving science, technology, and demand with up-to-date knowledge graph options, curation capabilities, and a team of experts to support your journey.
We Help You
Scale volume
Increase throughput without increasing headcount using explainable AI (XAI) and automated workflows.
Expand menu
Broaden your analysis to WGS or WES or standardize panels on a backbone assay. Analyze various variant types—SNVs, indels, short tandem repeats (STRs), copy number variants (CNVs), other structural variants, and mtDNA.
Launch assays
Implement a high throughput WGS, WES, virtual panel, or targeted panel workflow that is integrated into your lab's digital ecosystem.
Share curated knowledge
Leverage the power of collaboration to share knowledge across a private network of labs.
Key Features
Emedgene
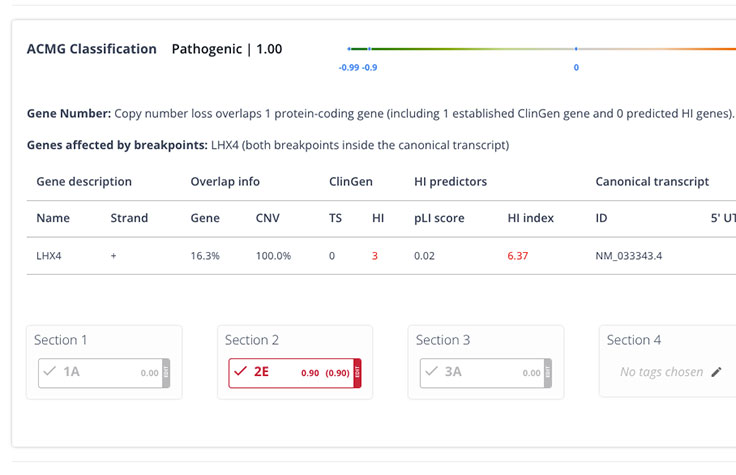
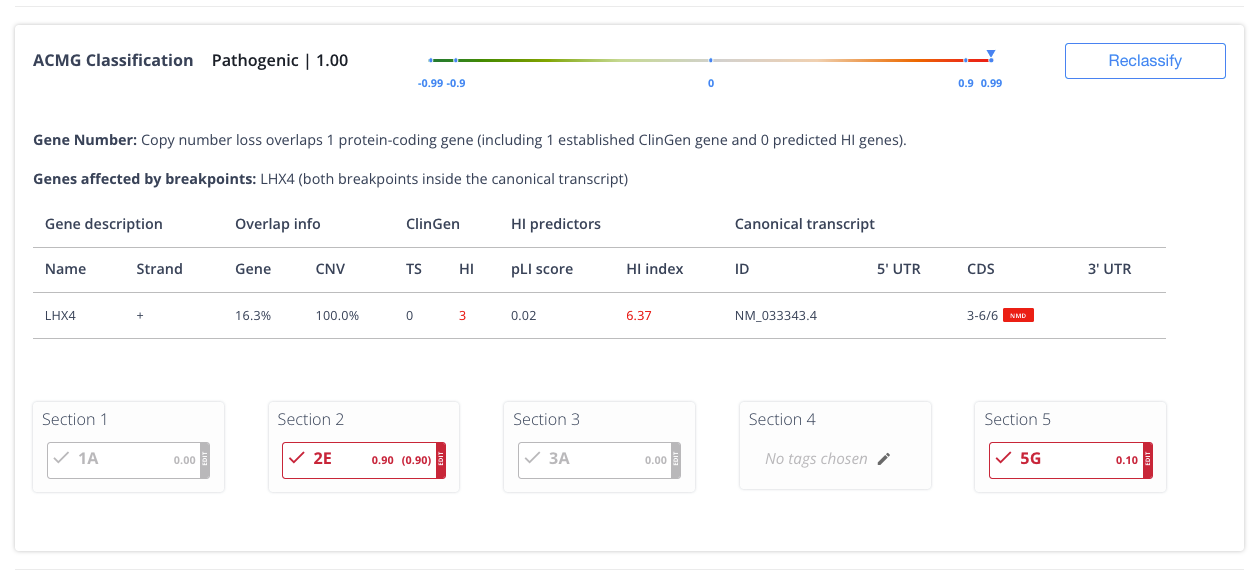
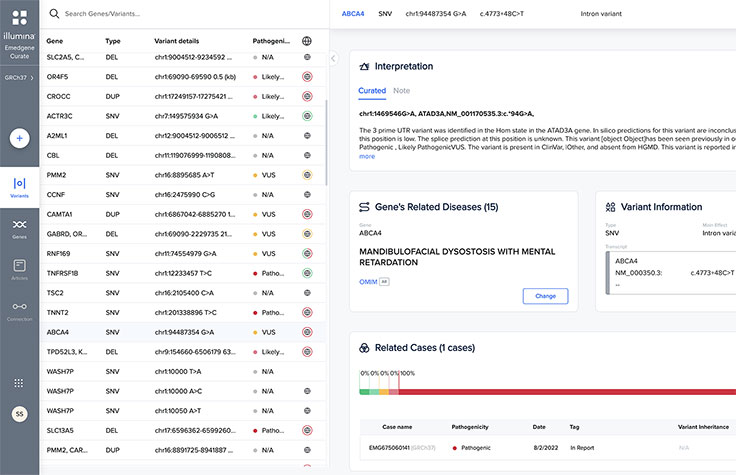
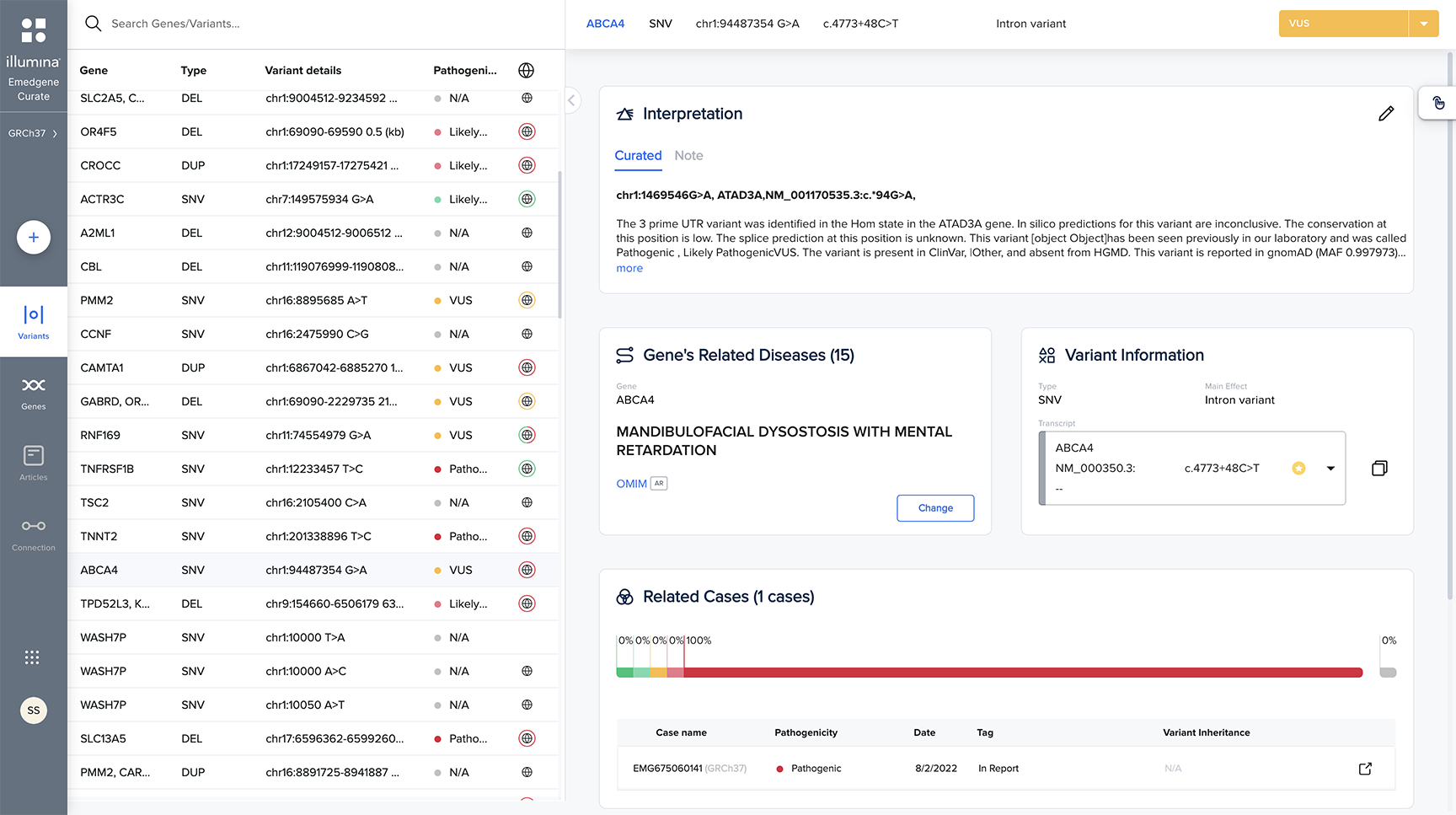
Explainable AI (XAI)
Never a black box. XAI prioritizes insights backed by evidence to increase workflow efficiency and confidence.
Automation
Maximize efficiency and scale by optimizing workflows for your standard operating procedures (SOPs) across test types, locking in your automated flow.
Powerful API interoperability
Integrate workflows with application programming interfaces (APIs), linking your tertiary analysis with laboratory information management systems (LIMS), storage, pipelines, and more.
Product Content
Brochure: Emedgene
Understand how automating insights can help you confidently scale your data operations.
Data sheet: Emedgene
Overview of the automated insights solution with AI-prioritization that can streamline dry lab workflows for WGS, WES, virtual panels, and targeted panels.
Customer Testimonials
"Emedgene’s machine learning simplifies the highly complex task of variant analysis, allowing us to handle more tests every day.”
Dr. Ray Louie, PhD
THOUGHT LEADERSHIP
Breaking the interpretation bottleneck
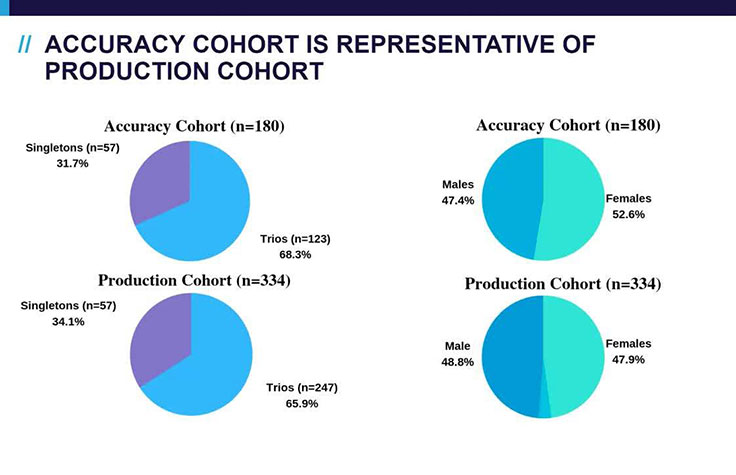
Dr. Linyan Meng, Division Director Clinical Interpretation, Baylor Genetics, presents the results of a research study demonstrating the utility of machine learning for interpretation in a 180-sample cohort. By automating their variant prioritization and classification processes, machine learning technologies support eliminating the bottleneck in genomic data interpretation.
Watch webinarKey Applications
Whole-genome sequencing (WGS)
WGS is the most comprehensive method for genetic disease testing and is increasingly applied to rare disease and other hereditary disease research.
Learn more about WGSVirtual panels
Virtual panels or “slices” can be created from a more comprehensive “backbone” assay that is standardized in the lab, such as WGS or WES.
Learn more about virtual panelsWhole-exome sequencing (WES)
WES evaluates the exons, or coding regions of the genome. WES can also serve as a standardized backbone assay for virtrual gene panels.
Learn more about WESTargeted sequencing
Analyze specific genes that are important for a hereditary disease or condition.
Learn more about targeted sequencingReady to connect with a genomic scientist?
Discuss your workflow to learn how you can streamline your NGS operations and power your lab for growth using Emedgene.
Request a demo